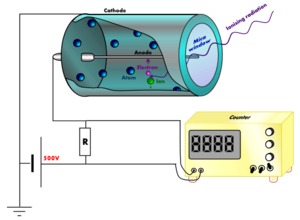
PRINCIPLE: Ionisation produced in the gas by nuclear radiations .
CONSTRUCTION:
* A metal tube with glass envelope (C) act as cathode.
*A fine tungsten wire (W) along the axis of the tube, act as anode.
* GM tube insulated from the wire is filled with an inert gas like argon at a low pressure.
* The radiations enter through a window (E) made of thin mica sheet.
*About 1000 volt is applied through a high resistance R (100 M ohm)
WORKING:
* Due to primary ionisations few ions produced are accelerated by high potential difference .
* These ions/electrons cause further ionisation and due to collisions, avalanche of electrons are produced.
* These electrons reaching the anode produces a current pulse.
* A high potential difference developed across R is amplified and operates an electronic counter.
* The counts in the counter is directly proportional to the Intensity of Ionising radiations.
* Ionisation of the gas does not depend on type of Incident radiations.
* Wilson's Cloud Chamber ,a particle detector records the visual observations of the tracks of charged particles.